A critical part of the college decision is affordability, and you can’t determine a college’s affordability for your family until you receive and review your financial aid offers. The different formats of financial aid offers can make it difficult to compare the financial aid awarded by colleges, and the offers themselves can vary widely.
To review your financial aid offers, you need to first understand the different types of information you might see in each one. Then, you can use MEFA’s College Cost Calculator to compare your offers to one another to make the most affordable college choice for your family. Here’s a guideline to different financial aid offer components.
1. Costs
The most helpful financial aid offers include the yearly costs of the school, such as tuition, fees, food and housing (if applicable), and an estimate of other expenses, such as books, supplies, and travel costs. These costs should be listed in the offer, in the documents that accompany the offer, or on the college website. If the school has not posted their costs for the upcoming year, then review last year’s costs as a benchmark.
2. Grants and Scholarships
In the offer, you will see any grants and scholarships that you have received. The terms “grant,” “scholarship,” and “award” are often used interchangeably, and all these terms represent direct funds that can be subtracted from the school’s costs and don’t need to be repaid. Learn more about different types of grants, scholarships, and other financial aid here.
Understand which funds were awarded based on your financial need and which were awarded based on merit, especially to know if and how funds may be available for all four years:
1. Need-Based Grants/Scholarships are based on the family’s finances and require that students submit the FAFSA® each year and meet Satisfactory Academic Progress standards. Changes in financial or household situations can sometimes result in an increase or decrease in these funds.
2. Merit Grants/Scholarships are based on the student’s achievements and often require a certain GPA or number of credits earned per semester or academic year and might have other requirements. Check the materials that accompanied the financial aid offer for these details.
3. Work-Study
Your financial aid offer may include federal work-study. Though your work-study award will list a dollar amount, you will not receive this money up front. Instead, this money is earned in paychecks received throughout the year through an on-campus job. Usually, students use the money earned through work-study to pay for miscellaneous personal expenses.
4. Loans
The most important point to understand about loans is that they need to be repaid, usually with interest. Not all loans that appear in a financial aid offer are financial aid. However, the most common education loans found in an offer, such as the Subsidized and Unsubsidized Federal Direct Loans, are considered financial aid. This is because they typically have:
- lower interest rates
- lower fees
- in-school deferment
- flexible repayment terms
- the ability for an 18-year-old with little credit and income to borrow without a co-signer
Some schools may list a Federal Direct PLUS Loan in the offer. This is not financial aid. It is a loan that a parent must apply and be credit approved for. The presence of a PLUS Loan in an offer is merely a suggestion of how to pay the college bill.
Note that students are not required to borrow any loans they receive. They are offered only as options to help pay the bill. If you decide to accept your Federal Direct Student Loan, and then, during the academic year, realize you no longer need the loan, you can cancel it at that point. You can also decline the Federal Direct Student Loan initially, and then accept it at any time during the academic year.
5. Private Scholarships
Any private scholarships that you received and reported to the financial aid office may be listed in the financial aid offer. If not, then keep any private scholarships that you received in mind when calculating your costs at each school.
Based on federal regulation, if the sum of your private scholarships and financial aid exceeds your financial aid eligibility, the financial aid office may need to adjust your financial aid offer. Contact your college’s financial aid office for more information.
6. Factors that Determined Your Financial Aid Eligibility
The eligibility factors used to calculate your financial aid may be listed in the offer, such as:
- student’s enrollment status
- planned housing arrangement
- number of people in your family
- number of family members attending college in the upcoming year
Make sure this information is accurate and notify the financial aid office of any errors or if changes occur during the upcoming school year.
When you deduct the available financial aid from the total cost of the college or university, the balance is your net cost, which is what you will have to pay. If you reviewed your financial aid offers and would like to pursue a reassessment of your financial aid eligibility, learn more about the appeal process here.
Below is a sample financial aid offer.
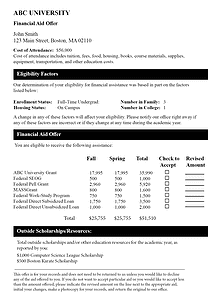
While financial aid offers can be confusing, they do contain lots of important information to help you make your college decision. Review them carefully, and read everything that you receive with the offer. If you still have questions, you can contact the financial aid office to ask. You can also call (800) 449-6332 or email [email protected] to ask a MEFA college planning team member any of your questions.









